National Nutrition Month – Mental Health and the Impact of Food | Smart TMS
March 10, 2020 - Smart TMS
Chocolate, crisps, alcohol and takeaways, we are all known to overindulge in these tasty foods. However, a Lancet study in 2017 found globally, 1 in 5 deaths were caused by unhealthy diets. As we enter National Nutrition Month, we at Smart TMS want to raise awareness of the importance of healthy eating. Food not only affects your physical health but equally as importantly your mental health too.
National Nutrition Month
National Nutrition Month aims to raise awareness about the importance of making informed food choices. The campaign focuses on educating people on the benefits of eating a balanced diet and helping them develop healthier lifestyles. In turn, encouraging people to choose healthier food options.
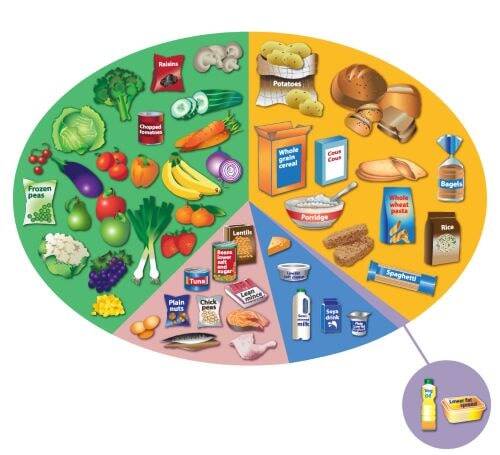
What Does A Healthy Diet Look Like?
A healthy diet consists of eating a variety of foods from each of the five main food groups, in order to consume a wide range of nutrients. The five main food groups are:
- Fruit and vegetables
- Starchy carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Dairy products
- Oils and spreads
How Do Our Food Choices Impact Our Mental Health?
Our mental health is just as important as our physical health; therefore, it is vital we fuel our bodies with the essential nutrients it needs. In 2014, a study found that individuals who ate a balanced diet rich in fruit and vegetables had higher levels of wellbeing, compared to those who didn’t. Highlighting the vital link between mental health and food.
In the UK, 1 in 6 people in any given week experience a common mental health problem such as depression and anxiety. Emerging research emphasizes how food can affect the likelihood of developing various mental health disorders such as depression. In 2017, a study found that individuals who had a diet characterized by a high intake of foods such as fruit, vegetables, fish and low- fat dairy products had a decreased risk of depression. In contrast, individuals with a diet consisting of low intakes of fruit and vegetables but high intakes of foods such as processed meat, sweets and high-fat dairy products had an increased risk of depression.
Healthy eating also shows promise for reducing depressive symptoms. In 2017, a study found that participants who had moderate-to-severe depression and who ate a healthy diet for 12 weeks, alongside nutritional counselling, had a reduction in their depressive symptoms including their mood and anxiety.
Emerging research suggests that a Mediterranean style diet also shows promise for reducing symptoms of depression. Recent research in 2019 found that a Mediterranean- style diet caused a reduction in participants depression which was sustained 6 months after the intervention. Highlighting that nutrition and the food we eat can have an impact on our mental health. A Mediterranean style diet typically consists of large quantities of fish, fruit, vegetables, fish oil, cereals and beans.
Top Tips to Eating Healthy
A healthy diet is an important factor contributing to your both your mental and physical health, therefore some ways you can eat healthier are:
- Eat breakfast;
- Avoid eating foods which affect your mood by causing your blood pressure to increase and then decrease rapidly in large quantities. Examples of these foods include but are not limited to sweets, fizzy drinks and alcohol;
- Drink plenty of water;
- Eat your five a day;
- Plan your meals and make dishes that include foods from variety of food groups;
- Get involved in cooking your healthy meals from scratch as this makes it more enjoyable. It is also great way to encourage your children to cook and eat healthy too;
- Make small changes to your diet gradually.
Gut Health and Depression
The primary function of your gut is the absorption of nutrients, digestion and excretion of waste. However, it is also believed that your gut communicates with your brain. Research has begun to suggest a link between the bacteria in your gut and mental health conditions such as depression. In 2019, a study found that depressed patients had lower levels of Coproccis and Dialister bacteria, compared to healthy controls, even when accounting for antidepressants.
Some bacteria in our gut helps regulate our mood. The gut contains 90% of the body’s serotonin. High levels of serotonin are associated with an elevated mood and low levels are associated with depression and feelings of sadness. It is thought our gut bacteria can influence levels of serotonin in the body by our gut bacteria producing its own serotonin. Therefore, it is important to eat a diet which helps maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in the gut, which in turn may help regulate your mood.
A balance of good and bad bacteria is important to maintain a healthy gut. Studies have shown that the balance of bacteria in your gut can affect your emotions, the way you process information and plays a role in mental health disorders. Probiotic foods contain good bacteria like the ones found in your gut and are thought to help restore healthy levels of gut bacteria and reduce depressive symptoms. In 2017, a review found that eating probiotic supplements alleviated depressive symptoms in individuals diagnosed with depression. This compelling evidence, if supported by further research could lead to treatments involving the use of probiotics to help treat depression.
Some foods which contain probiotics are:
- Yogurt
- Kefir
- Sauerkraut
IBS and Anxiety
Irritable bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common disorder which affects the large intestine which is a part of your gut. Some symptoms of IBS include:
- Pain
- Diarrhoea
- Constipation
- Bloating
The cause of IBS is not known but a factor which does play a role is the change of bacteria in your gut. The good bacteria in your gut is known as microflora, which play a key role in maintaining good health.
Anxiety and stress can affect the gut and in turn IBS. The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for your ‘fight’ or ‘fight’ mode. Both stress and anxiety can activate this system. When you’re feeling stressed or anxious this causes hormones linked to the gut’s healthy bacteria to be released which in turn can slow, stop or even cause overactivity in your gut. Consequently, homeostasis (maintaining a stable state) is not achieved which results in a disturbance between the brain and gut. Thus, triggering IBS.
It is estimated around 40-60% of those with IBS have a psychiatrics condition such as anxiety or depression. Therefore, it is important to know ways you can reduce IBS. Recent research in 2014 has shown that that probiotics are effective in reducing IBS symptoms. Highlighting that good nutrition can help relieve IBS, therefore it is important to eat a healthy diet. Some ways to reduce IBS are:
- Use fresh ingredients when cooking your meals
- Avoid foods which trigger your IBS
- Eat probiotics foods
- Exercise
How Can I Improve My Gut Health?
As even more research is suggesting that gut health is linked to your mental health, it is important to keep your gut healthy and functioning correctly. The diversity of bacteria in your gut is affected by what you eat. Some ways to improve your gut health are:
- Eat lots of fibre
- Eat more probiotic foods
- Avoid eating highly processed foods as these can suppress good bacteria and can increase levels of bad bacteria in your gut
- Eat a wide range of plant-based foods as there is a wide range of bacteria in the gut which all need different nutrients to function
Good nutrition is essential for both your physical and mental health. If you would like further information about how your diet affects your health and ways to make positive changes to your diet, please visit the websites below.










